VMware virtualization platform
What is vSphere?
vSphere delivers essential services for the modern hybrid cloud. The new vSphere has been rearchitected with native Kubernetes to run existing enterprise applications alongside modern containerized applications in a unified manner.
vSphere 7
A new generation of vSphere for traditional applications.
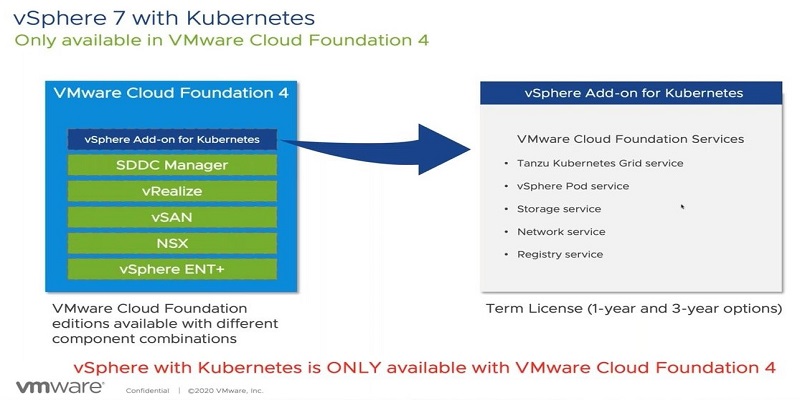
vSphere 7 with Kubernetes
The new generation of vSphere now supports modern containerized applications. vSphere 7 with Kubernetes is available through VMware Cloud Foundation.
vSphere Virtualization Platform
As the foundation of the VMware virtualization platform architecture, vSphere unifies the resources (including processors, memory, storage devices, and networks) in traditional data centers into the computing infrastructure. At the same time, it provides unified operation management tools for the infrastructure.
vSphere has two core elements: ESXi and vCenter Server.
| ESXi |
It is a virtualization platform in which you can create and execute virtual machines and virtual application devices. Although it can exist independently, it is recommended to form a cluster of virtualization platforms with vCenter Server. |
| vCenter Server |
It is a service, a unified operation management tool, which exists as a virtual machine. You can use this service to manage multiple hosts connected to the network and create pools for host resources. |
Why virtualize?
Bare metal server vs virtualization platform
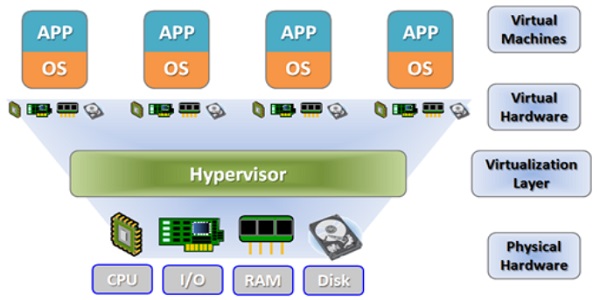
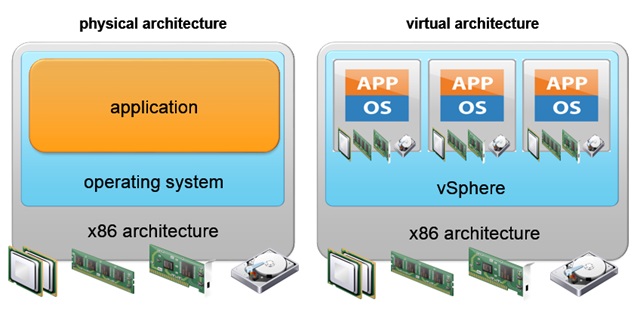 The composition of the virtualization platform
The composition of the virtualization platform
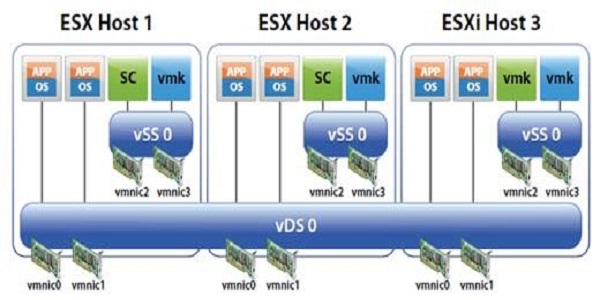
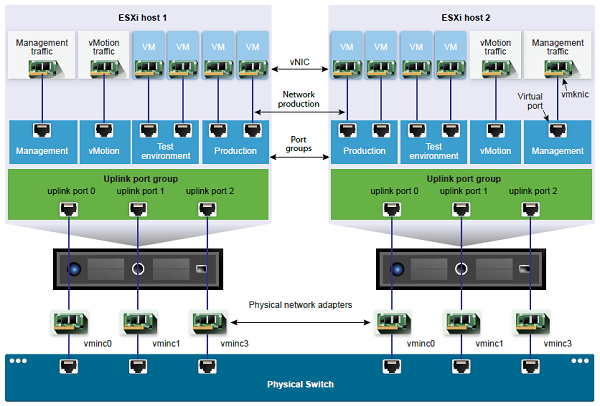
 Virtualized platform network
Virtualized platform network
 Comparison of ESXi server (virtualization platform) and vCenter server (management tool) in vSphere client (infrastructure)
Comparison of ESXi server (virtualization platform) and vCenter server (management tool) in vSphere client (infrastructure)
 vCenter server (Management tools)
vCenter server (Management tools)
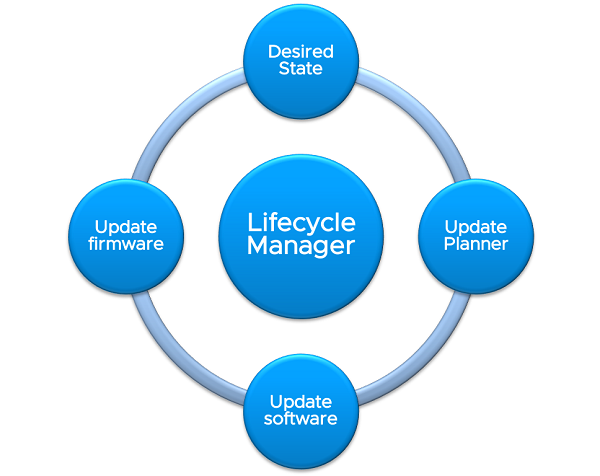
 Understand some of the key features of vSphere 7.0
. vSphere 7.0 introduced vSphere Lifecycle Manager, which is a centralized and simplified lifecycle management mechanism for VMware ESXi 7.0 hosts. Lifecycle management refers to the process of adding/updating/upgrading a host to retirement.
Understand some of the key features of vSphere 7.0
. vSphere 7.0 introduced vSphere Lifecycle Manager, which is a centralized and simplified lifecycle management mechanism for VMware ESXi 7.0 hosts. Lifecycle management refers to the process of adding/updating/upgrading a host to retirement.
. Strengthen the security of vSphere 7, adopt a built-in architecture that covers a wide range of layers, protect the security of infrastructure, data, and access from a more essential part, and provide a simplified, policy-driven management model.
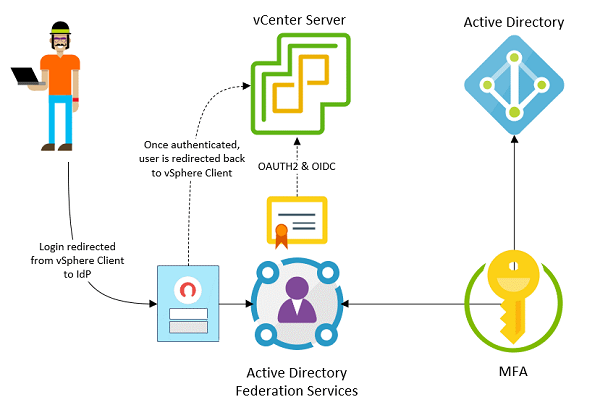
. You can use centralized authorization management to manage authorization for ESXi hosts, vCenter Server, vSAN clusters, and other VMware solutions.
. vSphere with Kubernetes is a platform that executes Kubernetes workloads (Pods) natively on the Hypervisor layer.
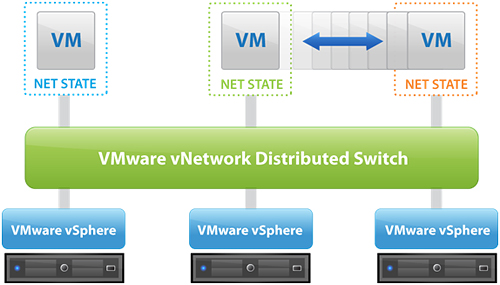
. Create vSphere Distributed Switch (vDS) and vSphere Standard Switch (vSS) network services, monitor the network to analyze the traffic between virtual machines (VMs) and hosts, and manage network resources.
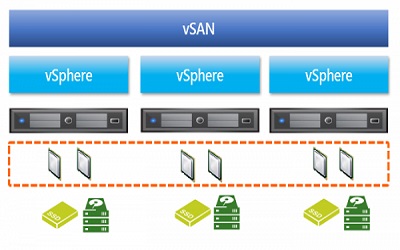
. Configure and use virtualization and software-defined storage area technology (vSAN) provided by ESXi and vCenter Server.
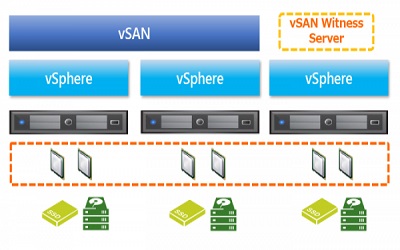
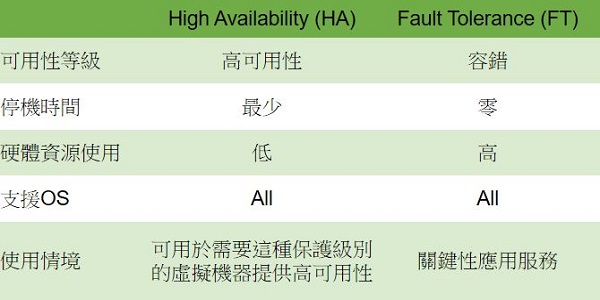
. Use vCenter High Availability (HA) to provide business continuity. vCenter HA provides failover protection for hardware and operating system outages in virtualized IT environments.
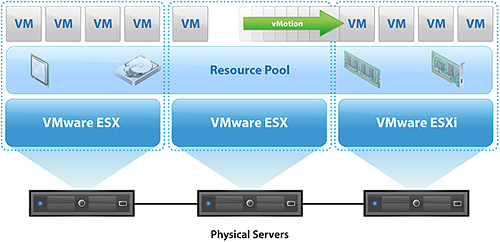
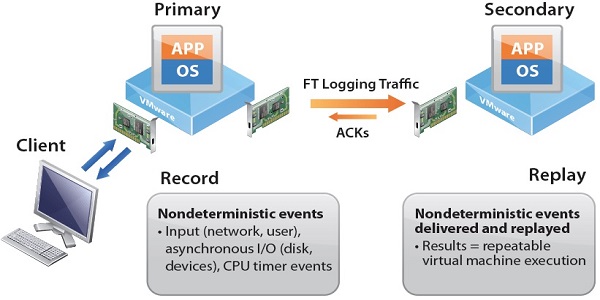
. Use vSphere Fault Tolerance (FT) to provide business continuity. If the host fails, Fault Tolerance will provide continuous protection for the virtual machine.
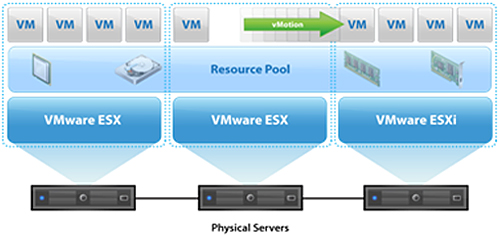
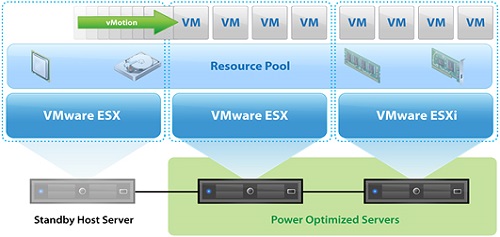
. Use resource pools, clusters, vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), vSphere Distributed Power Management (DPM) to manage and configure resources for ESXi hosts and vCenter Server.
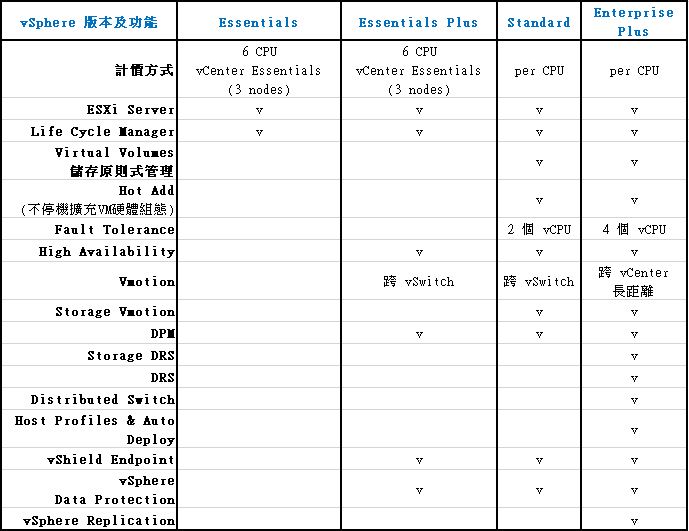
vSphere version comparison